Share market is a lucrative investment option for many. In India, apart from salary, rental income, and business income, you can earn money from the sale or purchase of securities. The money earned from the stock market is treated as Capital Gain income and you have to declare such income in ITR Filing and pay tax on it. In this article, you will understand the concept of Tax on Income earned from Share Market.
What is Capital Gain?
Capital Gain is income that you earn from selling any kind of capital assets including securities, either listed or unlisted.
For example, you sell a single stock of company ABC Limited for ₹100 which you bought for ₹80.
Here, you earned ₹20 and that is your capital gain. In simple words, it is the difference between the amount of selling price and cost price.
What is Capital Loss?
Capital Loss occurs when the selling price of an asset is less than the cost price of an asset i.e. shares, bonds, etc.
What are the types of Capital Gain?
There are mainly two types of Capital Gain in Share trading. The two types of Capital Gain are as follows:
 Long Term Capital Gains
Long Term Capital Gains
- LTCG(Long Term Capital Gains) are those profits that you earn selling a stock after holding the stock for more than twelve months.
- When it comes to equity investments, long-term means holding a stock for longer than a year.
- Long-term capital gains (LTCG) on equity shares taxed at the rate of 10%
- or If you have a long-term capital loss, it can only set off against long-term gains.
 Short Term Capital Gains
Short Term Capital Gains
- STCG(Short Term Capitals Gains) are those profits that you earn after selling a stock within the duration of twelve months.
- Thus, Short Term inequity means holding a stock for less than a year.
- You have to pay 15% Tax on Short Term Capital Gains regardless of your tax slab.
- The loss of short-term capital can be used to set off against both long-term capital gains and short-term capital gains.
Important Note: You can set off losses of your securities only if you do Income Tax Return Filing on time.

Different Types of Securities
Security is a type of financial asset that can be purchased and sold between people in the public market like the stock exchange.
People who own equity securities (e.g., shares) can make money when they sell their stocks. The companies issue securities in order to increase their financial resources.
Hence, companies can raise funds from the stock market or take business loans from banks
tax rates on income earned from various securities vary and need to pay while ITR Filing. But to do so, you must also know the different types of Securities that are mentioned below.
 Equity Shares
Equity Shares
- Ownership stake in a corporation is represented through equity securities.
- A shareholder is someone who invests in a company’s equity shares in order to own a stake in the company.
- Thus, An investor who has stock in a firm is referred to as a shareholder since they have stock in the company in proportion to their investment. Ideally, a company’s profits are dispersed proportionally to each shareholder’s equity stake.
- A company’s shares can be bought and sold on a specified stock market (exchange), such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) or Bombay Stock Exchange(BSE).
- Furthermore, Off-market transactions can be used to buy and sell shares of corporate entities that are not publicly traded.
 Debentures
Debentures
- Investors in a debenture get fixed interest payments for a specific period of time from a corporation that issues them.
- So, Debentures are divided into two categories: convertible and non-convertible (NCD). A non-convertible debenture (NCD) is a security that cannot be exchanged for stocks or shares or other forms of equity.
- Furthermore, NCD interest rates are determined by the issuer of the NCD.
- Residents, banks, main dealers, other Indian corporations, and unincorporated organizations all have the option to hold debentures investments.
 Bonds
Bonds
- Depending on the conditions of the bond, the authorized issuer pays the bondholders a debt and is required to pay interest (the coupon) to use and/or return the principal at a later point, known as maturity.
- Formally, bonds bind a party to return borrowed funds, plus interest, over a certain period of time (ex semi-annual, annual, sometimes monthly).
- In simple words, Bonds are like a contract between two parties where the issuer pays the fixed rate of interest periodically to the party who lends the money.
 Derivatives
Derivatives
- The term “derivatives” refers to financial agreements that derive their value from underlying assets. Derivatives’ value fluctuates constantly in response to market conditions.
- Derivatives contracts are based on the assumption that the value of the underlying asset will rise in the future, which is the fundamental motivation for engaging in them.
- Risk and reward are both increased by the use of leverage in derivatives.
- Among the most common types of derivatives are forward contracts, futures contracts, option contracts, and swap contracts.
 Future and Options
Future and Options
- A Future is a contract or agreement to buy or sell an underlying stock or another asset at a predetermined price on a particular date. Hence, there is an obligation.
- However, in the case of options, the buyer has no obligation to buy or sell the assets.
- Thus, Options and Futures, unlike bonds or stocks, do not help you make long-term returns; rather, they are designed to offset certain risks that result from continual price movement.
 Mutual Funds
Mutual Funds
- A Mutual Fund is a shared pool of money in which investors can place their money.
- As a result, the fund’s investment objective guides the way this total is allocated to various investments.
- This money in the Mutual Funds is utilized by Fund Managers to invest in assets such as stocks, bonds, money market, gold, real estate, etc.
- Money managers or fund managers run these funds, which invest in accordance with their stated investment aim in an effort to generate growth or appreciation for investors.
 ULIP
ULIP
- Life insurance product ULIP stands for Unit Linked Insurance Plan. Insurance and investing can be found together in a ULIP.
- ULIPs demand recurring premium payments, some of which are used to provide life insurance coverage.
- The remainder is combined with assets jointly funded from other policyholders and then continues to invest in investment products (i.e. equities and debt), much like mutual funds.
What are the Tax Rates on Capital Gains?
Capital Gains Tax is the tax on profits from the sale of a capital asset.
Hence, You must pay taxes on this gain or profit in the year in which the capital asset is sold since it falls under the heading of capital gain “income.”
Different types of Tax on Income Earned from Share Market

How to compute Capital Gains Tax?
Calculating capital gains tax on short-term gains is easier than on long-term gains. For short-term profits, the profit is added to overall income and afterward, the income tax is determined according to your tax slab.
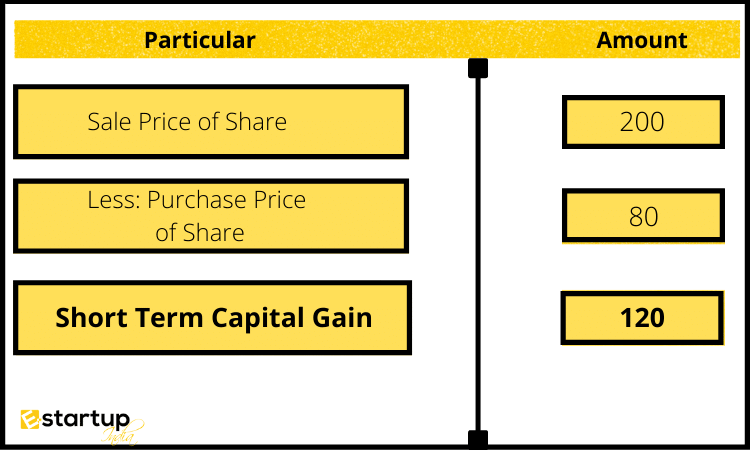
However, Calculating tax on long-term capital gains is a little more complicated. Because long-term capital assets are kept for a longer length of time, inflation is taken into account while determining long-term capital gains tax.
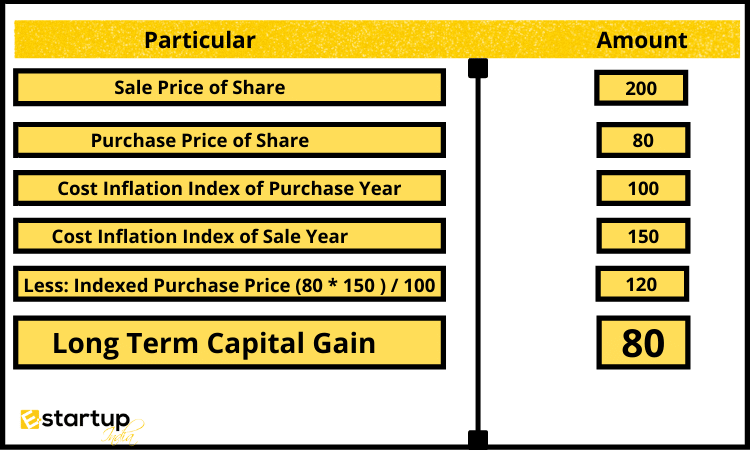
it’s advisable to hire a professional / Chartered Accountant for ITR Filing to pay tax on Income earned from Share Market.
Understand the Set Off and Carry Forward of Losses. Profits and losses are the two sides of the same coin. Of course, losses are difficult to swallow.
As a result, the Indian Income-tax legislation provides some advantages to taxpayers who experience losses as well.
The relief on the losses on Income earned from the share market is provided to you through provisions of Set-Off of Losses and Carry Forward of Losses.
What is Set Off of Losses?
Balancing losses against the year’s gain or revenue is known as a set-off loss adjustment.
In other words, Gain in one transaction can be set off against loss incurred in another transaction. It results in less tax on net gain [Total Gain – Total Loss].
What is Carry Forward of Losses?
Losses that are not offset against income in the current year might be carried over to the next future years and offset against income in future years.
Carry forward of losses situation occurs when losses of the year are greater than the gain of the same year.
These unadjusted losses might be carried forward to future years in order to set off against future earnings.
Losses can be carried forward for 8 years only and only if ITR filing is done on time.
Rules of Set-Off Losses and Carry Forward Losses
- Long-term capital losses can be adjusted only against long-term capital gains.
- Short-term capital losses can be set off against long-term capital gains as well as short-term capital gains
- The Act provides that losses may be rolled forward and set off only by the Assessee who incurred the loss.
- An Assessee must submit the Income Tax Return by the statutory due date.
What is the penalty for not filing ITR?
Penalty Amount can be levied up to ₹10,000/-. Furthermore, If you fail to pay your taxes through ITR Filing, you will be charged interest at 1% per month on any amount that is still unpaid. Lastly, you can also be imprisoned if the tax evasion amount exceeds ₹25 Lakhs.
Conclusion
Tax on Income earned from Share Market must be paid through ITR Filing. There are multiple Benefits of Filing Income Tax Return on Time and huge disadvantages if not done. You can understand more about Tax on Income earned from the share market and Income Tax Return Filing through a free consultation with our business advisors.
Moreover, If you want any other guidance relating to Income tax return Filing, please feel free to talk to our business advisors at 8881-069-069.
Download E-Startup Mobile App and Never miss the latest updates narrating to your business.
